Implicit domain meshing¶
mmg3d allows to discretize and optimize an implicitly defined surface (i.e. a surface defined by a level-set function).
Since mmg2d and mmg3d have lot of options in common, it is possible to refer to the 2d examples for:
isosurface discretization with mesh adaptation.
input materials preservation (multi-material mode).
bubble removal (small parasitic component deletion).
Standard level-set discretization¶
The starting point of this example is a mesh of a cube
(cube.meshb) and the discrete
level-set function defined at the mesh nodes
elephant.sol displayed below.
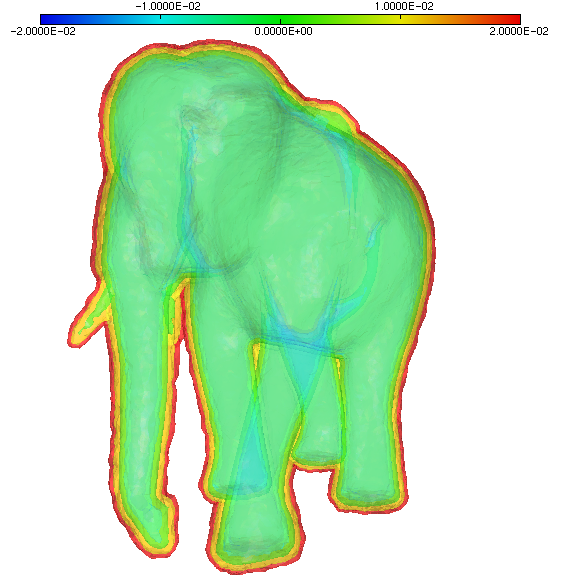
Input isosurfaces¶
To split the domain on the 0 value of the level-set function, run the
following command:
mmg3d_O3 cube -sol elephant.sol -ls -nr -hausd 0.001 -hgrad 1.3 -hmax 0.05
Solution file name is specified using the -sol option.
The
-lsoption states that the input.solfile is a level-set file and that mmg discretizes the implicit surface defined by the0isosurface of the level-set.A level-set function being a smooth function, ridges should not be detected and the
-nroption is used.The cube mesh bounding box size being [1 x 1 x 1], a Hausdorff parameter (-hausd option) of
0.001allows to have a good surface approximation.The authorized ratio between consecutive edges is increased using the -hgrad option.
The -hmax option ensures that no edges longer than 0.05 will be created.
The output mesh consists in two domains separated by a surface that is an optimized mesh of the initial implicit surface, as illustrated below.
Note that mmg impose the reference of the isosurface and domains:
The isosurface corresponds to reference 10.
Interior volume has reference 3.
Exterior volume outside has reference 2.
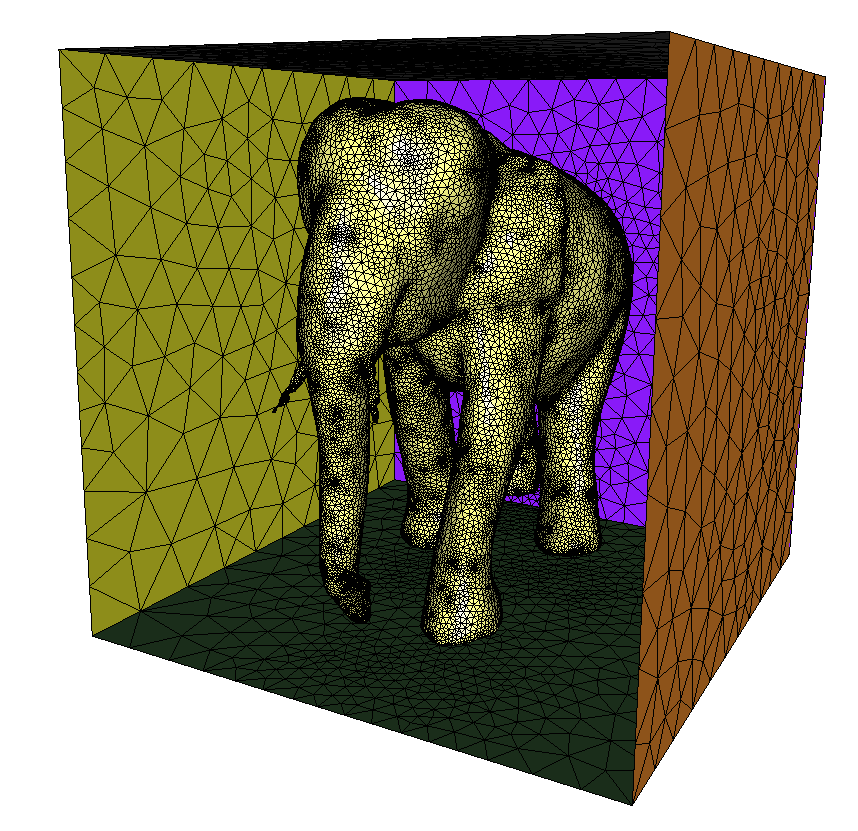
Output implicit surface mesh¶
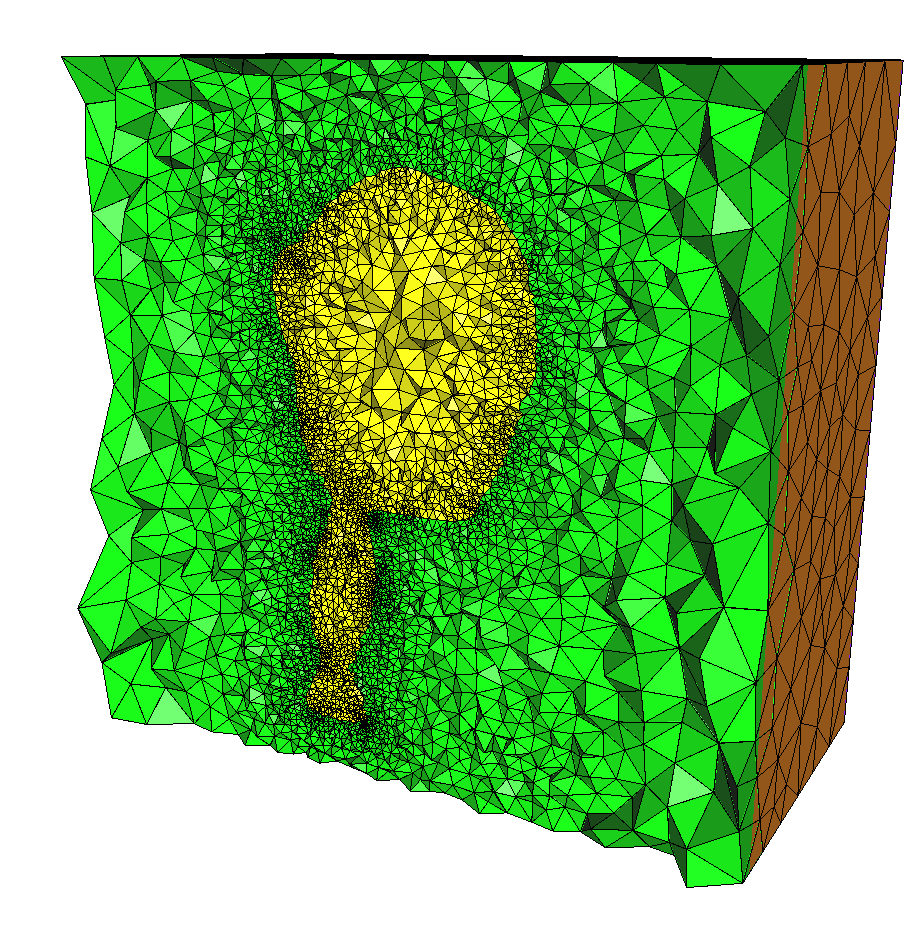
Cross-section view through output mesh¶
Preservation of one specific subdomain and analysis mode¶
mmg allows to save a given subdomain of a mesh containing multiple
subdomains using the -nsd option. For example, running mmg with the
following command saves the domain of reference 3 (in this example, it
corresponds to the elephant part of the output mesh):
mmg3d_O3 cube.o.meshb -noinsert -noswap -nomove -nsd 3
In this example, cube.o.meshb refers to the output mesh of the previous
command line. The coupling of -noinsert, -noswap and -nomove
options deactivates all remeshing operations, meaning that the mesh in
cube.o.mesh is only analyzed and not modified. The output is displayed
below.
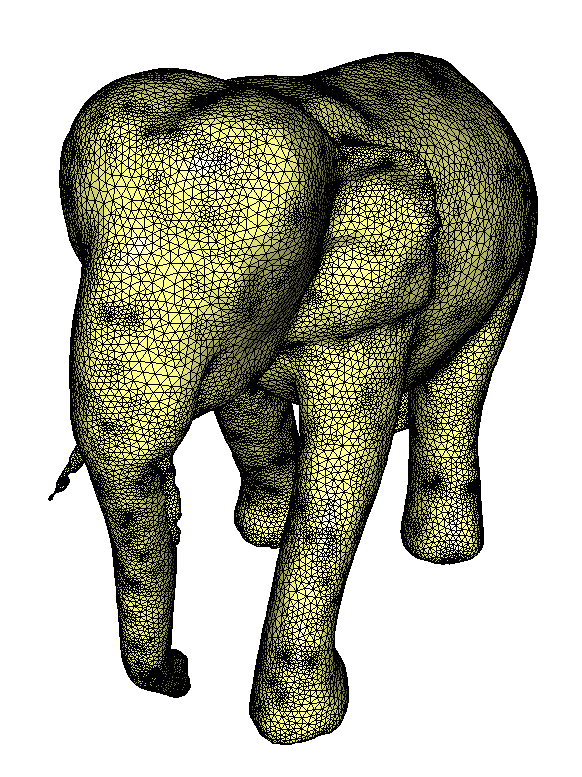
Saving only subdomain of reference 3 using the -nsd option¶
Boundary level-set splitting¶
With the -lssurf option, it is possible to split domain boundaries along
the level-set while leaving the interior of the mesh unsplit. In this example,
input data consist in the peninsula.mesh
meshfile and the peninsula.sol level-set
file, represented below:
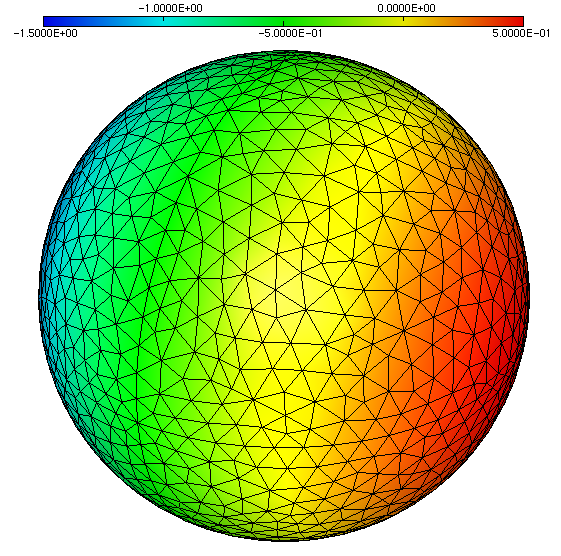
Initial data for surface level-set discretization¶
Level-set discretization of the surface only can be performed with the following command line:
mmgd3_O3 -lssurf peninsula.mesh
The result of this example is displayed below. With this option, mesh boundaries are split according to the input level-set function. Internal tetrahedra are not split. Note that all boundary references must be mapped in the reference file.
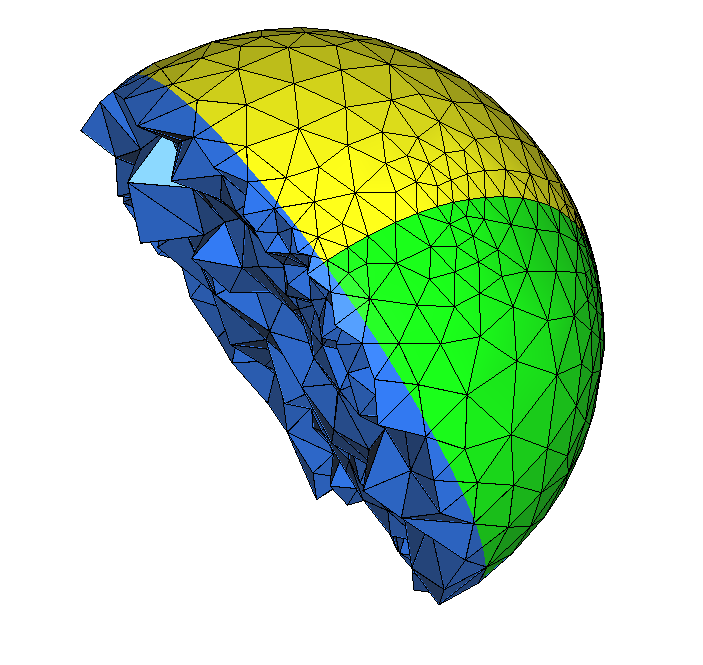
Boundaries split using -lssurf option¶
