Smooth surface remeshing¶
In this example, a rough mesh representing the thinker of Rodin
(rodin.mesh) is used to illustrate how to use
mmgs to improve its surface representation.
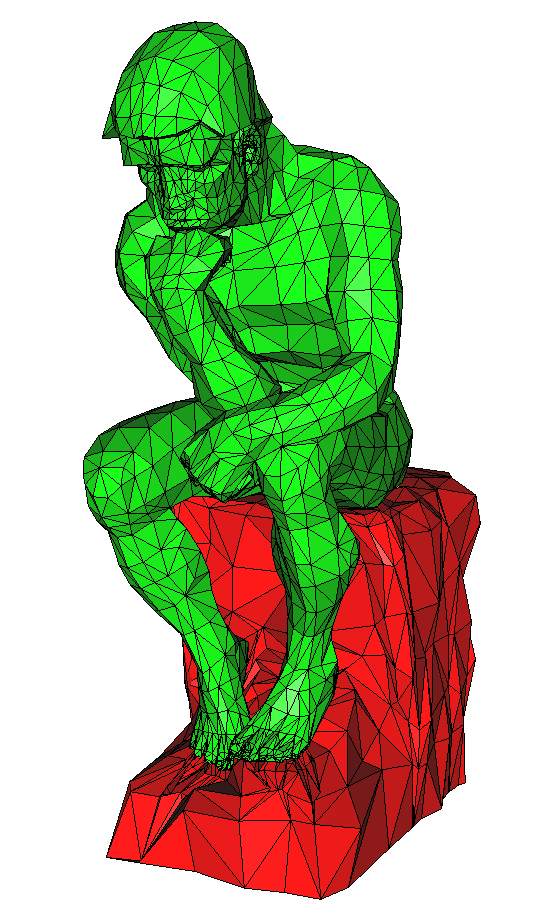
Rough input mesh of the thinker of Rodin¶
Two options may be used to do so:
The
-hausdoption can be used to control the surface approximation. The Hausdorff value is related to the mesh bounding box: the default value is set to 0.01 and is suitable for a bounding box of size [1 x 1 x 1]. In this example, the bounding box size is [0.6 x 0.4 x 1], which means that a Hausdorff value of 0.001 allows for a good surface representation.the
-nroption allows to specify that ridges should not be detected along the surface. By default, sharp edges, which are to be considered as geometric properties of the input mesh, are detected during the mesh analysis phase. Since the initial mesh of this example is of poor quality and that the ideal surface is smooth, this option allows to avoid detecting triangulation artifacts.
The output mesh is displayed below:
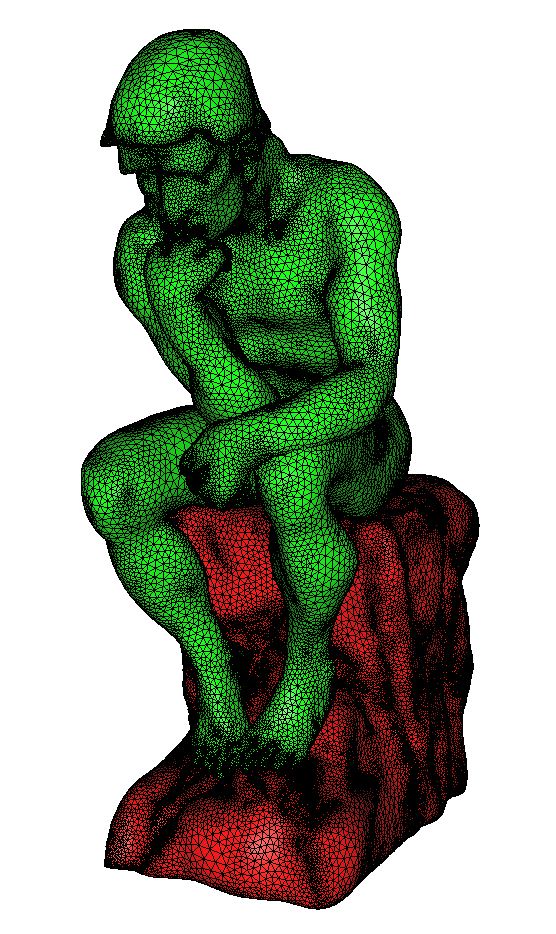
Smoothed output mesh of the thinker of Rodin¶
