About references¶
Generalities¶
In mmg, references (“ref” keyword in the API prototypes and Medit documentation) are integer values attached to each mesh entities (points, triangles, tetrahedra, …). This value is seen by mmg as the domain (or material) identification. It allows for exemple to identify:
boundary areas on which different boundary conditions will be applied
domains with different physical properties.
References are important values because mmg will try to preserve the interfaces between different references. An interface will be remeshed but with tangent and normal vector will be preserved.
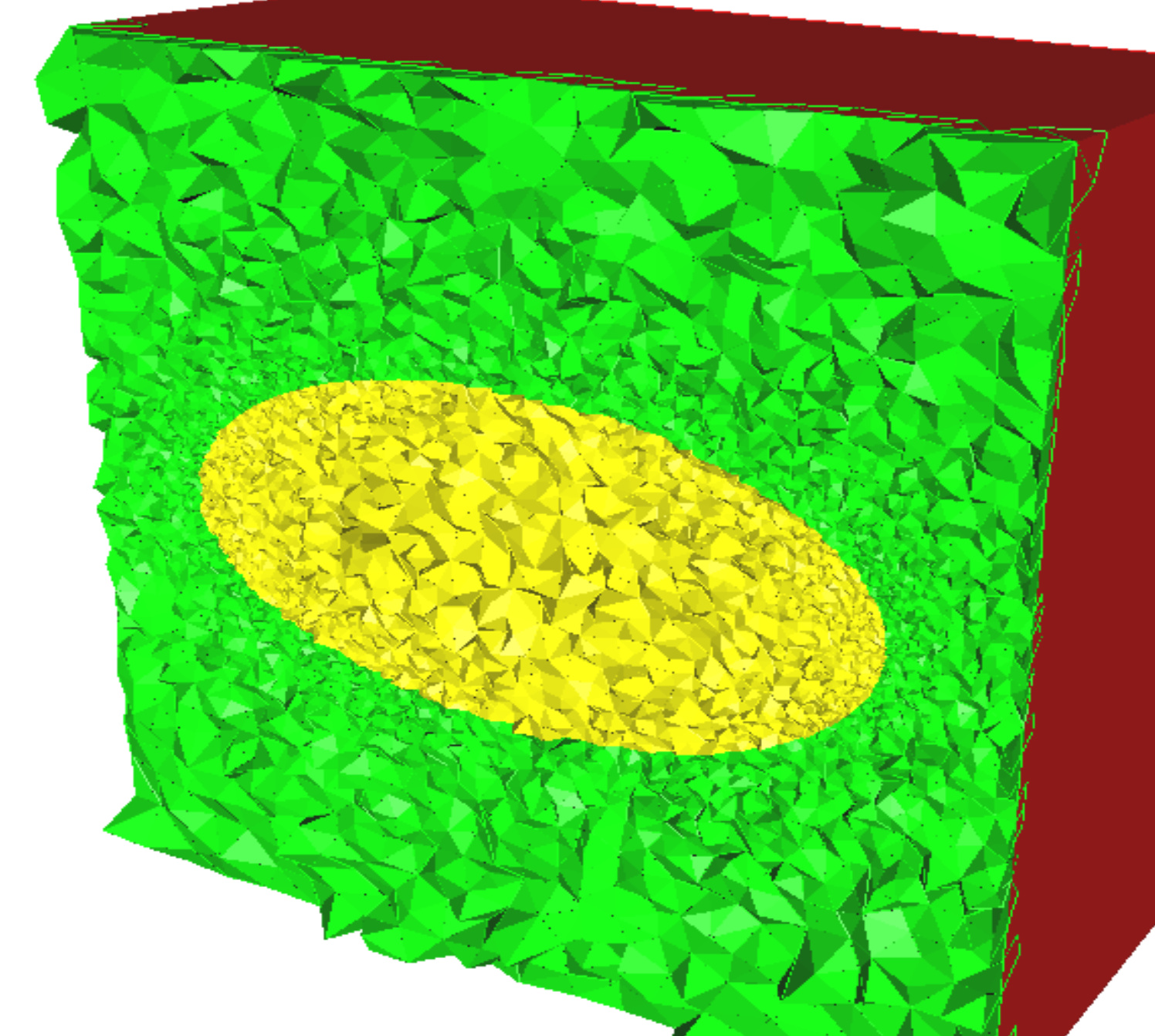
Example: mesh of an ellipsoid embedded inside a cube¶
The tetrahedra inside the ellipsoid have reference 3. In Medit, this reference is associated with the yellow color.
Tetrahedra outside the ellipsoid have reference 2, associated to the green color.
Triangles on the cube boundaries have reference 1 (represented in red).
Reference restrictions¶
Users must use nonnegative references. Negative references are used for debugging purposes by developpers and may lead to unexpected behaviour.
Interfaces between volume (tetrahedra in 3D or triangles en 2D) of same references are deleted since they are seen as lost surfaces inside one unique domain). To preserve such interfaces (3D only),
–opnbdyoption can me used. Note that it may slow down software execution.Input point references are preserved. As a consequence, collapses between points with different references may be refused. Moreover, new points are created with reference 0. If point references are not used, it is recommended to set it to 0 in input meshes.
References in level-set discretization mode¶
in progress
mmg references within Gmsh I/O¶
mmg references matches with the physical tag of gmsh.
